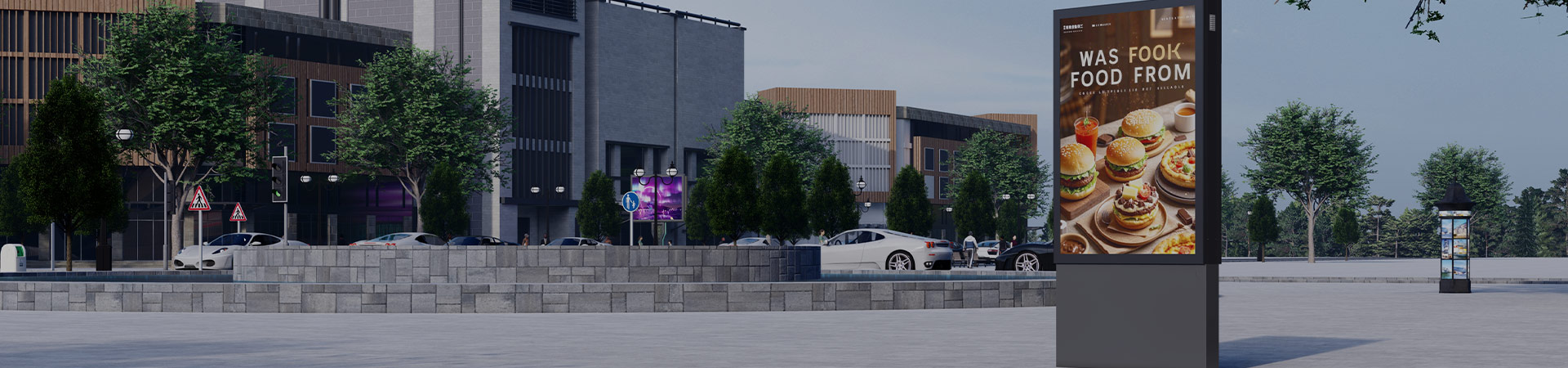
Urban projects—from transit hubs to downtown renewal—demand smart bus shelters that can withstand extreme wind conditions. A wind-damaged shelter not only disrupts public transit but also poses safety risks to commuters and pedestrians. With urban wind patterns becoming more unpredictable (due to climate change and tall building turbulence), choosing a wind-resistant smart bus shelter is critical for project success. Below is an expert guide to selecting shelters that meet 12-level wind resistance standards, integrate smart features, and align with urban design goals.
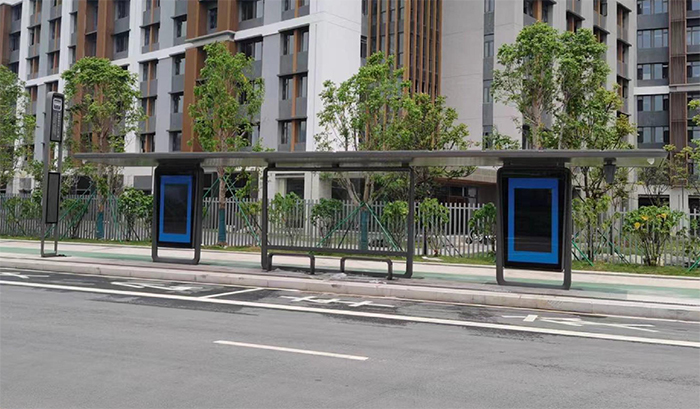

Why Wind Resistance Matters for Urban Smart Bus Shelters
Urban environments present unique wind challenges:
- Turbulence: Tall buildings create “wind tunnels” that amplify wind speeds at ground level.
- Storm frequency: Extreme weather events (hurricanes, typhoons) are becoming more common in urban areas.
- Safety risks: Wind-damaged shelters can injure commuters or damage nearby property, leading to liability for project owners.
- Cost savings: A wind-resistant shelter has a service life of 8+ years, reducing replacement and maintenance costs.
For urban projects, 12-level wind resistance (equivalent to 118–133 km/h winds) is the industry standard—this ensures the shelter can withstand severe storms and daily urban turbulence.
Key Factors to Choose Wind-Resistant Smart Bus Shelters
1. Structural Design: The Foundation of Wind Resistance
- Frame material: Choose 304 stainless steel or galvanized steel (minimum 3.0mm thick) for high tensile strength. Yeroo's urban shelters use 3.5mm galvanized steel frames, which resist bending and deformation in high winds.
- Frame structure: Opt for a “box-type” frame design (instead of open frames) for better wind load distribution. Yeroo's shelters include reinforced crossbeams and corner brackets to disperse wind pressure.
- Wind load calculation: Ensure the shelter is engineered to local wind standards (EN 1991 for Europe, ASCE for North America) in addition to 12-level wind resistance. Yeroo provides custom wind load reports for urban projects, accounting for building turbulence.
2. Roof and Panel Design: Minimize Wind Resistance
- Roof shape: Sloped or curved roofs (instead of flat roofs) reduce wind drag. Yeroo's urban shelters use a 30° sloped roof to deflect wind and prevent uplift.
- Panel material: Lightweight but durable materials (anti-UV polycarbonate panels) reduce the shelter’s wind load. Avoid heavy glass panels, which increase stress on the frame.
- Panel installation: Secure panels with wind-resistant fasteners (stainless steel bolts with lock nuts) to prevent them from blowing off. Yeroo’s panels are sealed with silicone to reduce wind noise and prevent water intrusion.
3. Smart Features: Integrate Without Compromising Wind Resistance
Urban smart bus shelters require features like real-time transit info and wireless charging—ensure these don't weaken wind resistance:
- Screen mounting: Mount digital screens flush with the frame (avoid protruding mounts) to reduce wind drag. Yeroo's screens use recessed enclosures that maintain the shelter's aerodynamic design.
- Bench and fixtures: Secure benches and charging ports to the frame with heavy-duty bolts. Avoid loose or detachable components that can become windborne debris.
- Solar panels: If using solar power, mount panels low on the roof (to reduce wind load) and secure them with reinforced brackets. Yeroo’s solar-powered urban shelters have wind-tested solar panel mounts.
4. Certification and Testing: Prove Wind Resistance
Don't rely on marketing claims—demand tangible proof of wind resistance:
- Wind tunnel test reports: Request reports from accredited labs (e.g., SGS) confirming 12-level wind resistance. Yeroo’s shelters undergo wind tunnel testing to simulate urban turbulence.
- Structural integrity certificates: Ensure the shelter’s frame and components meet international standards (ISO 9001, EN 12600).
- Project case studies: Choose a supplier with wind-resistant shelter projects in urban areas. Yeroo has delivered 8,000+ wind-resistant shelters to cities like Dubai, Mexico City, and Shanghai.
Case Example: Yeroo's Mexican Transit Hub Project
A Mexican city needed 80 smart bus shelters for a downtown transit project, facing 12-level winds and urban turbulence from tall buildings. Yeroo’s solution:
- 12-level wind-resistant shelters with 3.5mm galvanized steel frames and sloped roofs.
- Recessed digital screens, wireless charging ports, and real-time transit info.
- Wind tunnel test reports and local certification for municipal.
- Result: The shelters withstood two severe storms (120+ km/h winds) with zero damage, ensuring uninterrupted transit service and commuter safety.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Prioritizing aesthetics over wind resistance: A sleek design is important, but not at the cost of structural integrity—Yeroo balances urban design with wind resistance.
- Ignoring urban turbulence: Standard wind resistance tests don’t account for building turbulence—demand custom wind load calculations.
- Choosing lightweight materials: Thin steel or plastic frames may look modern but fail in high winds—invest in 3.0mm+ steel.
Next Steps: Select Wind-Resistant Shelters for Your Urban Project
Yeroo's wind-resistant smart bus shelters are engineered for urban environments, with 12-level wind resistance, smart features, and urban-friendly designs. Our team will:
1. Assess your project’s wind conditions (including urban turbulence from nearby buildings).
2. Provide a custom shelter design with wind load calculations and test reports.
3. Deliver and install shelters with minimal disruption to urban traffic and pedestrians.
Contact Yeroo today to get a personalized quote and ensure your urban smart bus shelter project is safe, durable, and compliant—even in extreme winds.
 Address:North Tower 904,New World Times Center,Guangyuan Dong Road ,Guangzhou,China
Address:North Tower 904,New World Times Center,Guangyuan Dong Road ,Guangzhou,China
 Address:No.23 Qianjinzhong Road,Guanyao, Shishan Town,Nanhai District,Foshan, China
Address:No.23 Qianjinzhong Road,Guanyao, Shishan Town,Nanhai District,Foshan, China
 Phone: +86 13826225776
Phone: +86 13826225776
 Email:3d@3dyeroo.com
Email:3d@3dyeroo.com